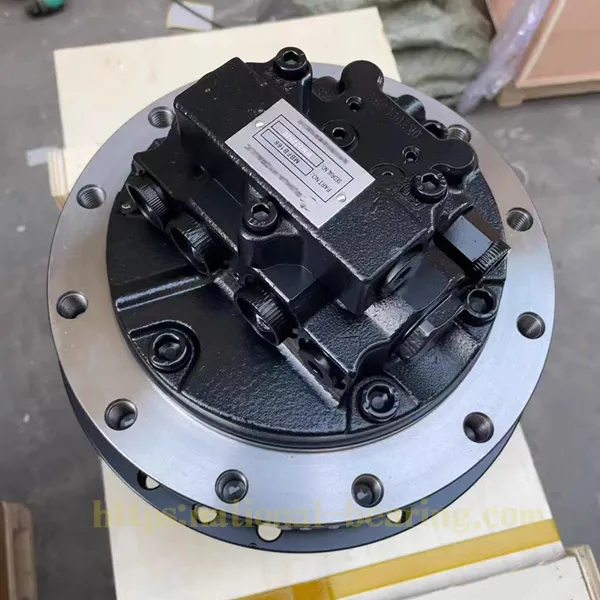

Excavator track motors are fundamental components that ensure the smooth and efficient movement of the machine. Understanding how these motors work can help operators maintain their equipment better and ensure optimal performance.
Excavator track motors, also known as final drives or travel motors, are hydraulic motors that power the movement of the tracks. These motors are essential for the mobility and maneuverability of the excavator, enabling it to traverse various terrains with ease.
The excavator’s hydraulic system is the heart of its operation. It includes a hydraulic pump, hydraulic fluid, valves, and actuators. The hydraulic pump generates the necessary pressure to move the hydraulic fluid through the system. The fluid then travels through valves that regulate its flow and direction, ultimately reaching the hydraulic motors and cylinders.
The hydraulic motors, including the track motors, convert the hydraulic energy into mechanical energy. This conversion allows the excavator to perform various tasks, such as moving the tracks, swinging the arm, and operating the bucket.
Excavator track motors consist of several key components, including the hydraulic motor, gear reduction system, and final drive assembly.
The operation of hydraulic motors in excavators is a complex process that involves several steps. Understanding these steps can provide valuable insights into how excavator track motors work.
The hydraulic pump generates high-pressure hydraulic fluid, which flows through the hydraulic system to the track motors. The flow and pressure of the hydraulic fluid are regulated by control valves, which ensure that the right amount of fluid reaches the motors at the right time.
The pressurized hydraulic fluid enters the hydraulic motor through an inlet port. Inside the motor, the fluid acts on a series of pistons or vanes, causing them to move. This movement generates rotational energy, which is transferred to the motor’s output shaft.
The output shaft of the hydraulic motor is connected to the gear reduction system. This system consists of multiple gears that reduce the high-speed, low-torque output of the motor into low-speed, high-torque output. The gear reduction system ensures that the excavator tracks receive the necessary force to move the heavy machine efficiently.
The gear reduction system typically includes planetary gears, which are arranged in a configuration that allows for significant torque multiplication. The reduced-speed, high-torque output is then transmitted to the final drive assembly.
The final drive assembly transmits the torque from the gear reduction system to the sprocket. The sprocket is a toothed wheel that engages with the track links, driving the track forward or backward.
As the sprocket rotates, it moves the track links, causing the entire track to move. The movement of the tracks propels the excavator forward or backward, allowing it to navigate various terrains and perform different tasks.
Excavator track motors rely on sophisticated control systems to operate efficiently. These systems regulate the flow and pressure of hydraulic fluid, ensuring that the motors receive the right amount of energy to move the tracks.
Modern excavators are equipped with electronic control units (ECUs) that monitor and control various aspects of the hydraulic system. The ECU receives input from sensors and operators, processing this information to adjust the flow and pressure of hydraulic fluid to the track motors.
The ECU ensures that the track motors operate smoothly and efficiently, even under varying load conditions. It can also provide diagnostic information, alerting operators to potential issues with the hydraulic system or track motors.
Sensors play a crucial role in the operation of excavator track motors. These sensors monitor various parameters, such as hydraulic fluid pressure, temperature, and motor speed. The data collected by these sensors is sent to the ECU, which uses it to make real-time adjustments to the hydraulic system.
Feedback mechanisms ensure that the track motors receive the right amount of hydraulic fluid at the right pressure. This feedback loop helps maintain optimal performance, reducing wear and tear on the motors and other components.
Operators control the movement of the excavator tracks using joysticks or pedals. These controls send signals to the ECU, which adjusts the flow and pressure of hydraulic fluid to the track motors accordingly.
The operator’s input determines the speed and direction of the tracks. The ECU processes this input and makes the necessary adjustments to ensure smooth and precise movement.
Proper maintenance and troubleshooting are essential to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of excavator track motors. Regular maintenance can prevent issues and identify potential problems before they become serious.
Regular inspections are crucial for maintaining the health of excavator track motors. Operators should inspect the track motors and related components for signs of wear, damage, or leaks. Key areas to inspect include:
Proper lubrication and fluid maintenance are essential for the smooth operation of excavator track motors. Operators should follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and fluid types.
When issues arise with excavator track motors, troubleshooting can help identify and resolve the problem. Common issues and their potential causes include:
Advancements in technology continue to drive innovation in excavator track motors. These advancements aim to improve efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and enhance operator comfort and safety.
One of the most significant trends in the construction industry is the move towards electrification and hybrid systems. Electric and hybrid excavators use electric motors and batteries to power the tracks and other components, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering emissions.
Electric and hybrid excavators offer several benefits, including reduced noise, lower operating costs, and improved efficiency. As battery technology continues to advance, the adoption of electric and hybrid excavators is expected to increase.
Modern excavators are equipped with advanced control systems that use artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms to optimize performance. These systems can analyze data from sensors and make real-time adjustments to the hydraulic system, improving efficiency and reducing wear and tear on components.
AI and ML algorithms can also provide predictive maintenance insights, identifying potential issues before they become serious. This proactive approach to maintenance can reduce downtime and extend the lifespan of excavator track motors.
Remote monitoring and telematics systems allow operators and fleet managers to monitor the performance of excavator track motors in real-time. These systems use GPS and wireless communication technologies to transmit data from the excavator to a central monitoring platform.
Remote monitoring and telematics can provide valuable insights into the health and performance of excavator track motors, enabling operators to make informed decisions about maintenance and operation. These systems can also alert operators to potential issues, allowing for timely intervention and reducing the risk of costly breakdowns.
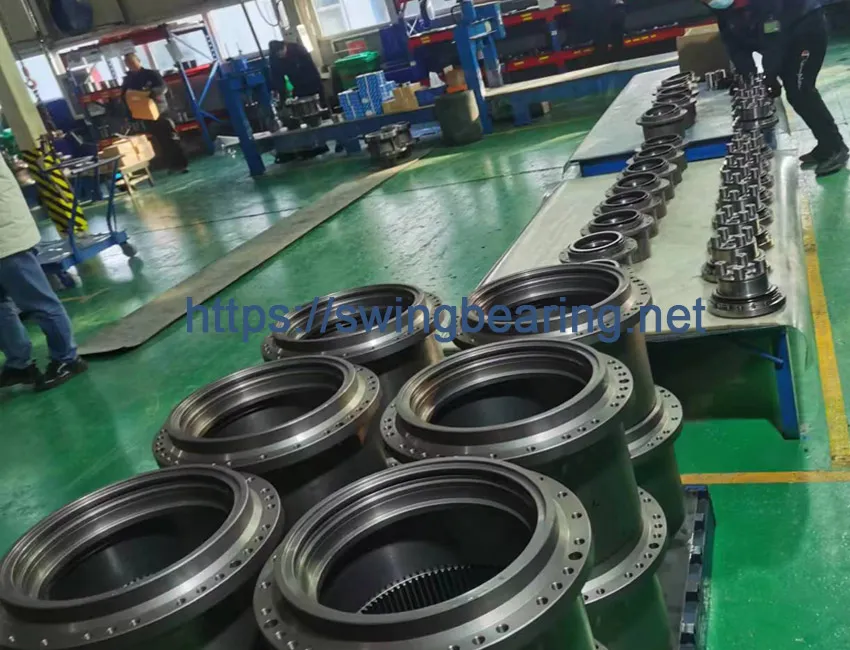
The construction industry is increasingly focused on sustainability, and this trend extends to the manufacturing of excavator track motors. Manufacturers are exploring the use of sustainable materials and processes to reduce the environmental impact of their products.
For example, some manufacturers are using recycled materials and environmentally friendly lubricants in the production of hydraulic motors and final drive assemblies. Additionally, advances in manufacturing processes, such as additive manufacturing (3D printing), are enabling more efficient and sustainable production methods.
Excavator track motors are essential components that enable the smooth and efficient movement of excavators. These hydraulic motors convert hydraulic energy into mechanical energy, driving the tracks and allowing the excavator to navigate various terrains.
Understanding how excavator track motors work, including the role of hydraulic systems, control units, and feedback mechanisms, can help operators maintain their equipment and ensure optimal performance. Regular maintenance, proper lubrication, and timely troubleshooting are crucial for the longevity and efficiency of track motors.

As technology continues to advance, the future of excavator track motors looks promising. Electrification, advanced control systems, remote monitoring, and sustainable manufacturing are just a few of the trends shaping the industry. By staying informed about these developments, operators and fleet managers can make informed decisions and embrace innovations that improve efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and enhance overall performance.